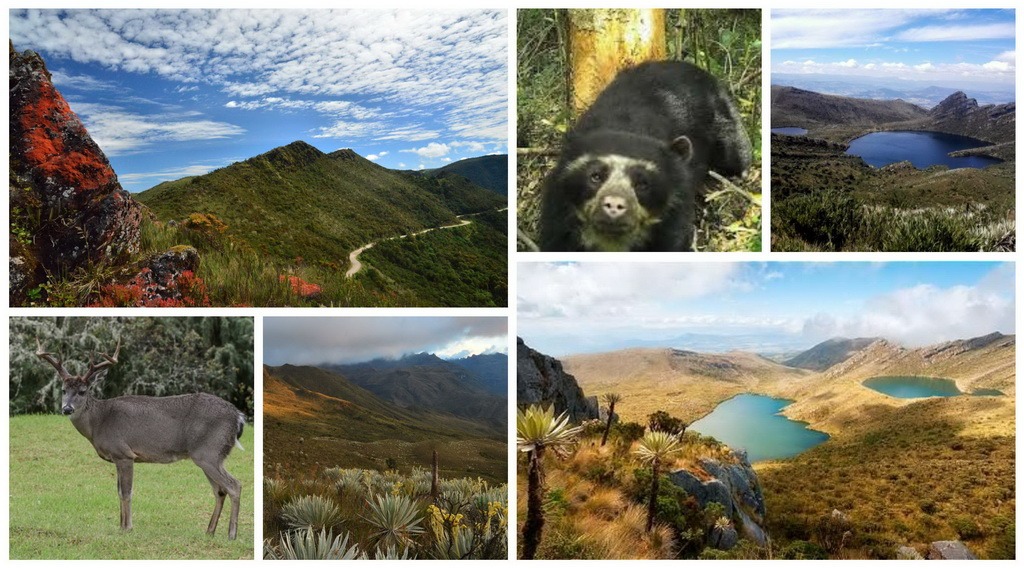
Colombia is one of the 10 countries in the world with the greatest biodiversity. It concentrates almost 70% of all the planet’s ecosystems in just 10% of its territory, thanks in part to its two oceans, the Andes and the Amazon.
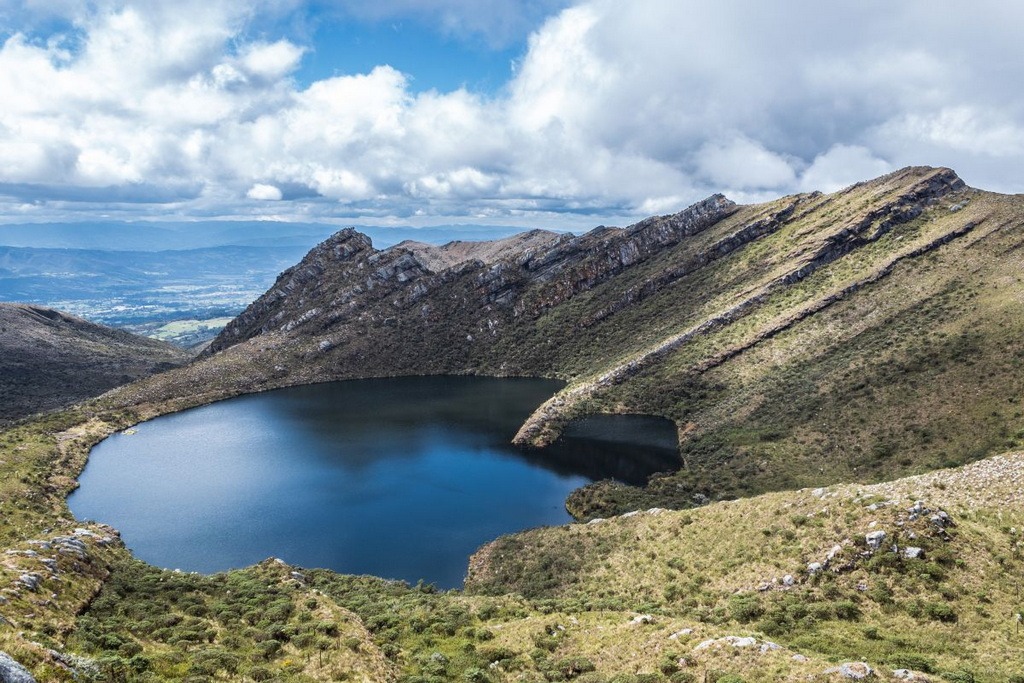
Chingaza National Park is a natural and cultural treasure located in the center of the Colombian Andes, between 800 and 4050 meters above sea level. Its surface area covers 76,600 hectares.
It was the home of the indigenous Muiscas and Guayupes, civilizations that developed around 1000 years ago and whose demise was precipitated shortly after the Spanish conquest (around 1550). Today, it is home to some of the Andean flora and fauna.
Its predominant ecosystems are the high Andean forests and the paramos (high altitude neo-tropical biotopes). This is a very humid region with a cold climate, an abundant and unique flora of over 2,000 species, and large lakes. The fauna consists mainly of large birds (condors, eagles), spectacled bears, deer, tapirs and various types of fox. Pumas and ounces are also sometimes found.